gRPC routing¶
The GRPCRoute resource allows you to match on gRPC traffic and direct it to Kubernetes backends. This guide shows how the GRPCRoute matches traffic on host, header, and service, and method fields and forwards it to different Kubernetes Services.
The following diagram describes a required traffic flow across three different Services:
- Traffic to
foo.example.comfor thecom.Example.Loginmethod is forwarded tofoo-svc - Traffic to
bar.example.comwith anenv: canaryheader is forwarded tobar-svc-canaryfor all services and methods - Traffic to
bar.example.comwithout the header is forwarded tobar-svcfor all services and methods
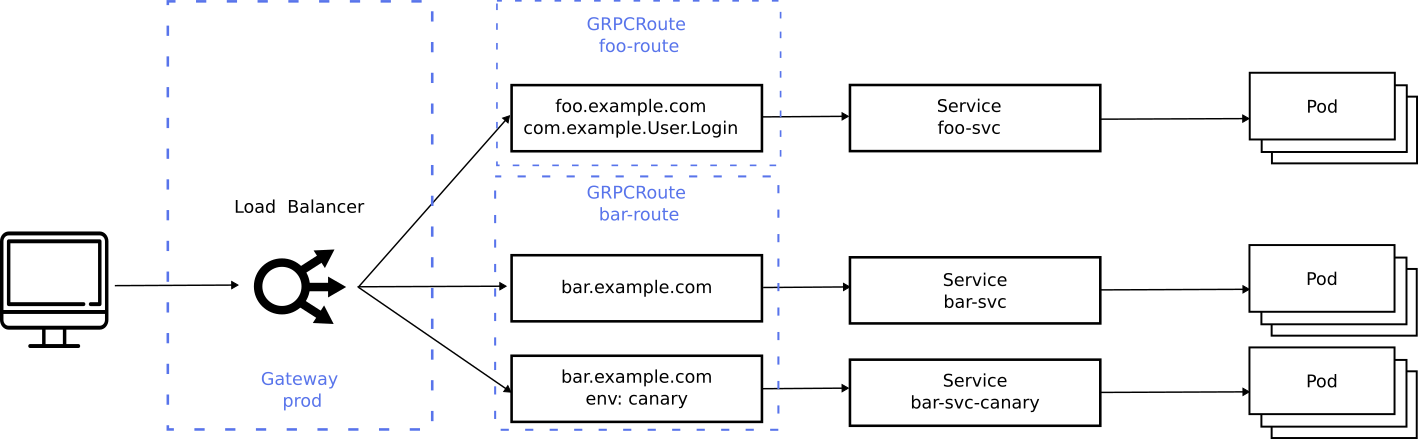
The dotted lines show the Gateway resources deployed to configure this routing
behavior. There are two GRPCRoute resources that create routing rules on the
same prod Gateway. This illustrates how more than one Route can bind to a
Gateway which allows Routes to merge on a Gateway as long as they don't
conflict. GRPCRoute follows the same Route merging semantics. For more
information on that, refer to the documentation.
In order to receive traffic from a Gateway, a GRPCRoute resource
must be configured with ParentRefs which reference the parent gateway(s) that it
should be attached to. The following example shows how the combination
of Gateway and GRPCRoute would be configured to serve gRPC traffic:
apiVersion: gateway.networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Gateway
metadata:
name: example-gateway
spec:
gatewayClassName: example-gateway-class
listeners:
- name: grpc
protocol: HTTPS
port: 50051
tls:
certificateRefs:
- kind: Secret
group: ""
name: example-com-cert
---
apiVersion: gateway.networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: GRPCRoute
metadata:
name: example-route
spec:
parentRefs:
- name: example-gateway
hostnames:
- "example.com"
rules:
- backendRefs:
- name: example-svc
port: 50051
A GRPCRoute can match against a single set of hostnames.
These hostnames are matched before any other matching within the GRPCRoute takes
place. Since foo.example.com and bar.example.com are separate hosts with
different routing requirements, each is deployed as its own GRPCRoute -
foo-route and bar-route.
The following foo-route will match any traffic for foo.example.com and apply
its routing rules to forward the traffic to the correct backend. Since there is
only one match specified, only requests for the com.example.User.Login method to
foo.example.com will be forwarded. RPCs of any other method` will not be matched
by this Route.
apiVersion: gateway.networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: GRPCRoute
metadata:
name: foo-route
spec:
parentRefs:
- name: example-gateway
hostnames:
- "foo.example.com"
rules:
- matches:
- method:
service: com.example
method: Login
backendRefs:
- name: foo-svc
port: 50051
Similarly, the bar-route GRPCRoute matches RPCs for bar.example.com. All
traffic for this hostname will be evaluated against the routing rules. The most
specific match will take precedence which means that any traffic with the env:
canary header will be forwarded to bar-svc-canary and if the header is
missing or does not have the value canary then it will be forwarded to bar-svc.
apiVersion: gateway.networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: GRPCRoute
metadata:
name: bar-route
spec:
parentRefs:
- name: example-gateway
hostnames:
- "bar.example.com"
rules:
- matches:
- headers:
- type: Exact
name: env
value: canary
backendRefs:
- name: bar-svc-canary
port: 50051
- backendRefs:
- name: bar-svc
port: 50051
gRPC
Reflection
is required to use interactive clients such as
grpcurl without having a local copy
of the target service's protocol buffers present on your local filesystem. To
enable this, first ensure that you have a gRPC reflection server listening on
your application pods, then add the reflection method to your GRPCRoute. This
is likely to be useful in development and staging environments, but this should
be enabled in production environments only after the security implications have
been considered.
apiVersion: gateway.networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: GRPCRoute
metadata:
name: foo-route
spec:
parentRefs:
- name: example-gateway
hostnames:
- "foo.example.com"
rules:
- matches:
- method:
service: com.example.User
method: Login
backendRefs:
- name: foo-svc
port: 50051
- matches:
- method:
service: grpc.reflection.v1.ServerReflection
backendRefs:
- name: foo-svc
port: 50051